data-structures-and-algorithms-java
Graphs
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of nodes and edges. The nodes are sometimes also referred to as vertices and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph.
Challenge
Implementing the graph, and should include the following methods:
- add node
- add edge
- get nodes
- size
API
- add node()
Arguments: value Returns: The added node Add a node to the graph - add edge()
Arguments: 2 nodes to be connected by the edge, Returns: nothing Adds a new edge between two nodes in the graph Both nodes should already be in the Graph - get nodes()
Arguments: none Returns all of the nodes in the graph as a collection (set, list, or similar) get neighbors Arguments: node Returns a collection of edges connected to the given node Include the weight of the connection in the returned collection - size()
Arguments: none Returns the total number of nodes in the graph
Challenge Summary
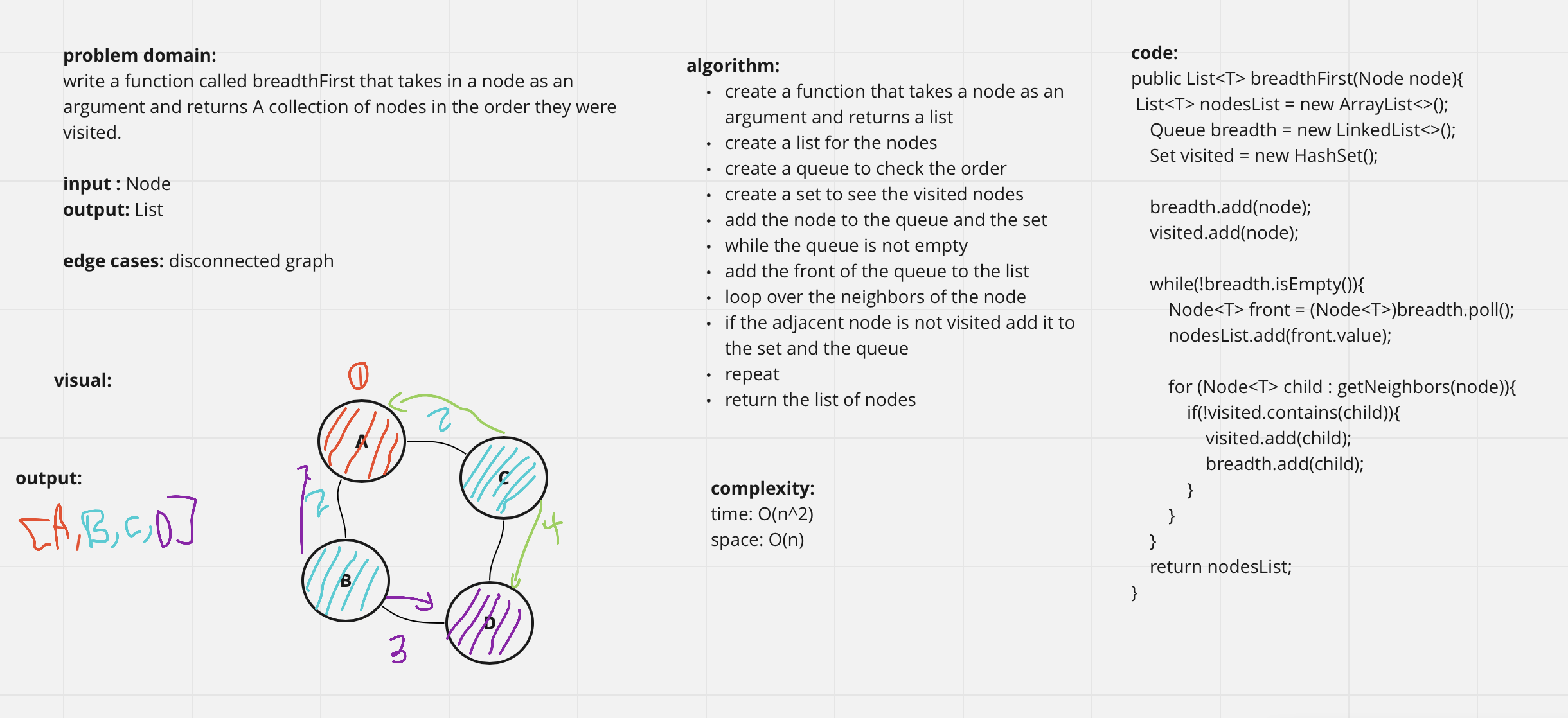
write a function called breadthFirst that takes in a node as an argument and returns A collection of nodes in the order they were visited.
Whiteboard Process
Approach & Efficiency
complexity:
time: O(n^2)
space: O(n)
Solution
Graph graph = new Graph();
Node n1 = new Node("A");
Node n2 = new Node("B");
Node n3 = new Node("C");
Node n4 = new Node("D");
graph.addNode(n1);
graph.addNode(n2);
graph.addNode(n3);
graph.addNode(n4);
graph.addEdge(n1,n2);
graph.addEdge(n1,n3);
graph.addEdge(n1,n4);
graph.breadthFirst(n1)
output: [A, B, C, D]
Depth First Traversal
DFS (Depth-first search) is technique used for traversing tree or graph. … In this traversal first the deepest node is visited and then backtracks to it’s parent node if no sibling of that node exist.
Challenge
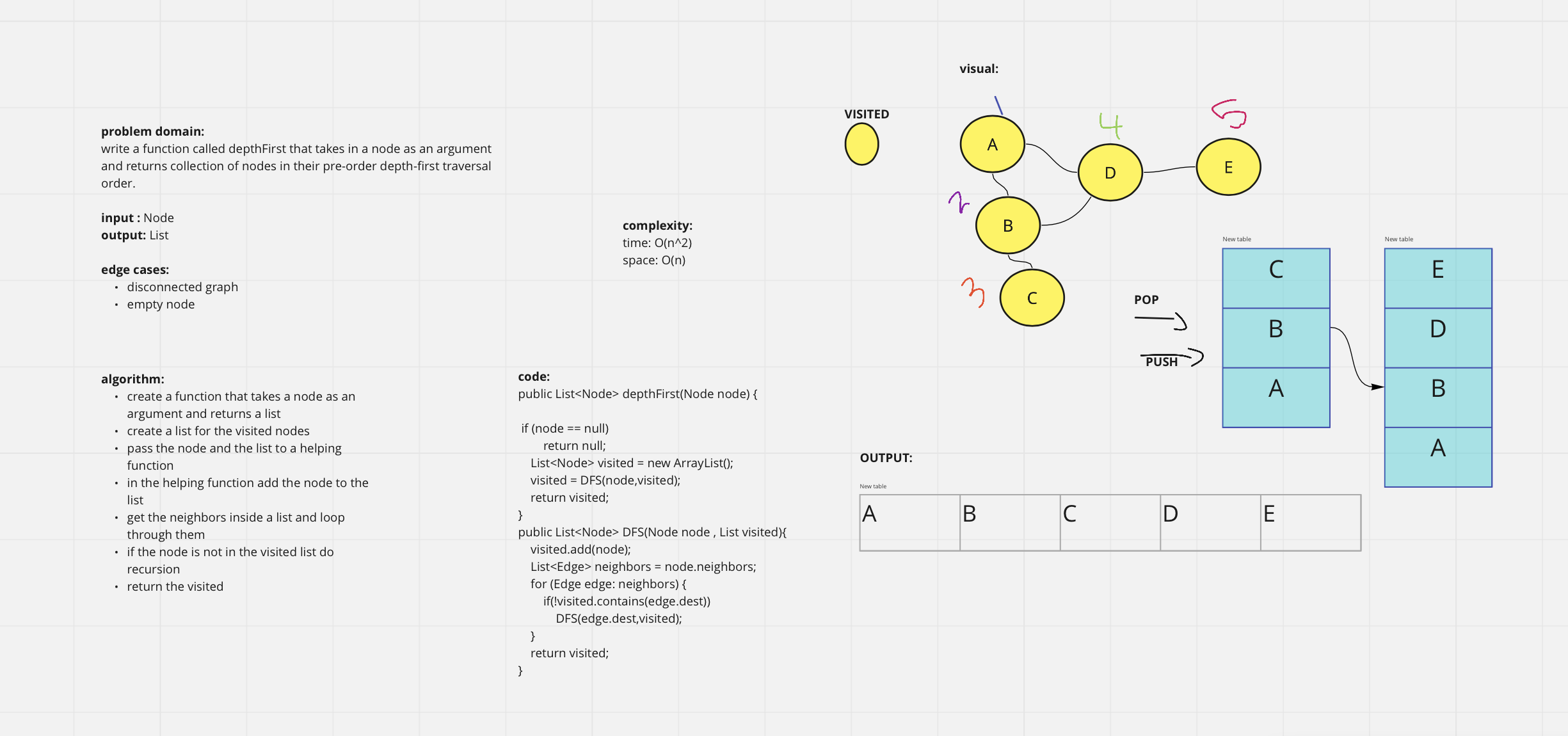
write a function called depthFirst that takes in a node as an argument and returns collection of nodes in their pre-order depth-first traversal order.
Approach & Efficiency
complexity:
time: O(n^2)
space: O(n)
Solution