data-structures-and-algorithms-java
Singly Linked List
The singly linked list is a linear data structure in which each element of the list contains a pointer which points to the next element in the list. Each element in the singly linked list is called a node. Each node has two components: data and a pointer next which points to the next node in the list
Challenge
- create a Node class
- create a LinkedList class
- create three methods
-
- insert method
-
- include method
-
- toString method
Approach & Efficiency
| method | Time complexity | Space complexity |
|---|---|---|
| insert method | O(1) | O(1) |
| include method | O(n) | O(1) |
| toString method | O(n) | O(n) |
API
- insert method : to insert a node to the linked list
- include method : to check whether the value given is indicated as a node in linked list
- toString method : representing all the values in the Linked List
Challenge Summary
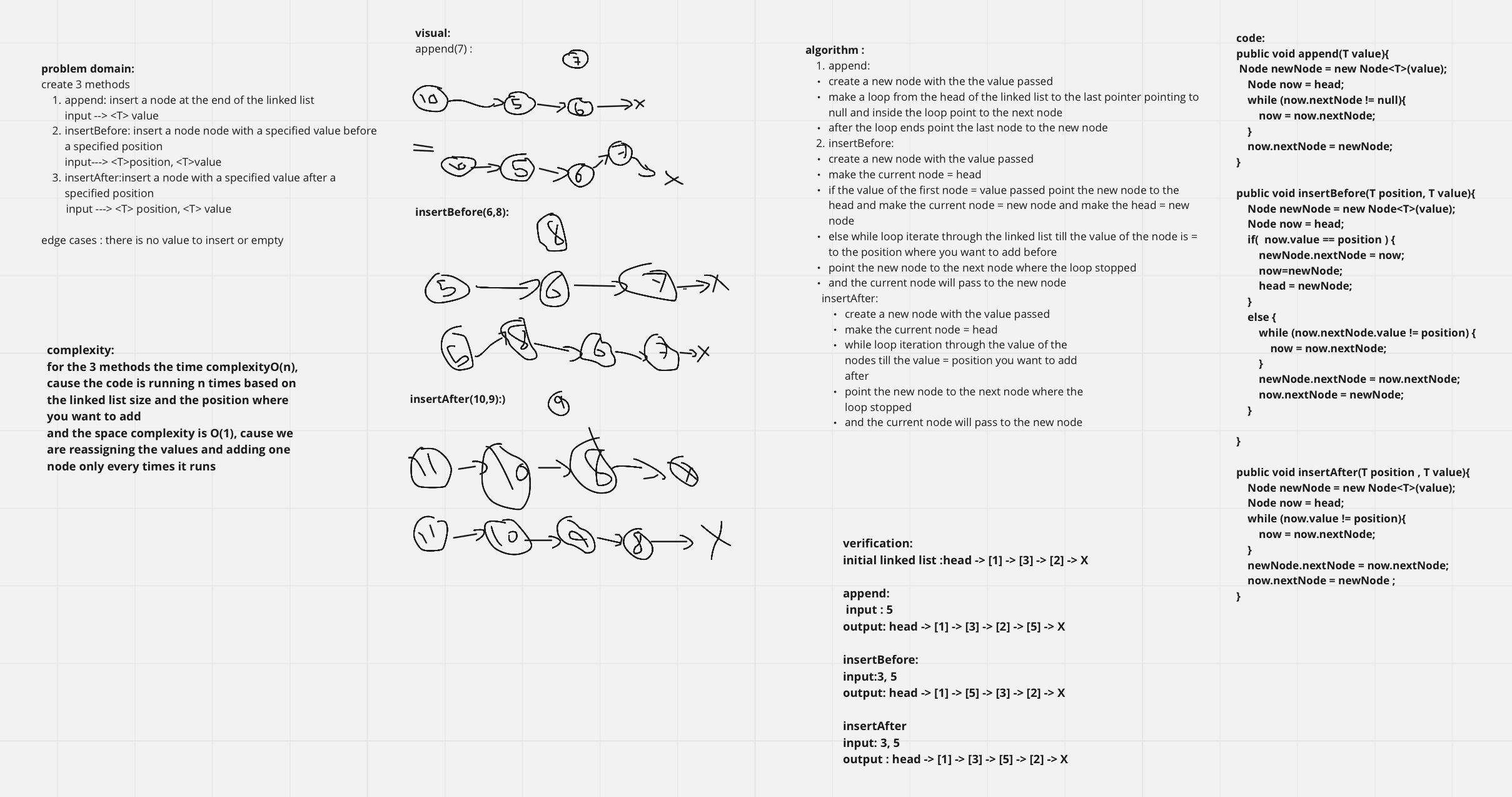
create 3 methods
- append: insert a node at the end of the linked list
- input –>
value
- input –>
- insertBefore: insert a node node with a specified value before a specified position
- input—>
position, value
- input—>
- insertAfter:insert a node with a specified value after a specified position
- input —>
position, value
- input —>
Whiteboard Process
Approach & Efficiency
complexity:
for the 3 methods the time complexityO(n), cause the code is running n times based on the linked list size and the position where you want to add
and the space complexity is O(1), cause we are reassigning the values and adding one node only every times it runs
Solution
- create a new linked list
- call the method using the instance
initial linked list :head -> [1] -> [3] -> [2] -> X
append:
input : 5
output: head -> [1] -> [3] -> [2] -> [5] -> X
insertBefore:
input:3, 5
output: head -> [1] -> [5] -> [3] -> [2] -> X
insertAfter:
input: 3, 5
output : head -> [1] -> [3] -> [5] -> [2] -> X
Challenge Summary
create a method that takes an integer (k) as an argument and return the value of the nodes k’th place from the tail
Whiteboard Process

Approach & Efficiency
time complexity : O(n), cause here we have two arrays which are not nested the first on will run n times based on the length of the linked list and the second one will run n times based on the valued passed so its O(n+n) = O(n) space complexity: O(1) , cause we are not storing variables more than once , and only reassigning
Solution
- count the length of the linked list using a while loop
- if the value passed (k) is bigger than the length of the linked list return the value is larger than the linked list
- else make a loop till the length - n -1
- when the loop finishes the current will be on the kith node from the last
- return the value of the k’th node
verification: linked list: { 10 } -> { 6 } -> { 22 } -> { 34 } -> { 5 } -> { 10 } -> { 20 } -> NULL
Input : 3
output : 34
input: 8
output: the number passed is bigger than the linked list
Challenge Summary
create a function that takes in Arguments: 2 linked lists and Return: Linked List, Zip the two linked lists together into one so that the nodes alternate between the two lists and return a reference to the head of the zipped list.
Whiteboard Process

Approach & Efficiency
Complexity:
time complexity:O(n)
space Complexity: O(n)
Solution
verification:
input:(list1,list2)
list1:head -> [1] -> [3] -> [2] -> X
list2:head -> [5] -> [9] -> [4] -> X
output: head -> [1] -> [5] -> [3] -> [9] -> [2] -> [4] -> X